|
| |
SONO RIPORTATI I CAMPI DI INTERESSE ED I PRINCIPALI TEMI DI RICERCA POSTI IN
ESSERE DALLA NOSTRA ASSOCIAZIONE SIA COME PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR CHE IN
COLLABORAZIONE CON PARTNER ISTITUZIONALI:
SVILUPPO E VALIDAZIONE DI PROTOCOLLI AD
IMPEDENZA MIOGRAFICA PER LO STUDIO DELLA ARCHITETTURA MUSCOLARE NELLE
PATOLOGIE NEUROMUSCOLARI |
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
Assessing Skeletal Muscle
Architecture and neuromuscular disease with multifrequency electrical
impedance myography.

|
Electrical impedance
myography (EIM) is a new non-invasive technique for the evaluation of
neuromuscular disease that relies upon the application and measurement
of high-frequency, low-intensity electrical current.
EIM assesses
disease-induced changes to muscle’s normal composition and architecture,
including myocyte atrophy and loss, edema, reinnervation, and the
deposition of endomysial connective tissue and fat.
With application of
single-frequency electrical current, EIM can be used to help grade the
severity of neuromuscular disease. Assessing electrical impedance across
a spectrum of applied frequencies and with current flow at multiple
orientations relative to the major muscle fiber direction can provide a
more complete picture of muscle condition.
EIM holds the promise
of serving as an indicator of disease status, thus being useful in
clinical trials work and in monitoring effectiveness of treatment in
individual patients; ultimately, it may also find diagnostic application.
Ongoing efforts have
been focused on obtaining a deeper understanding of the basic mechanisms
of impedance change, studying EIM in a variety of clinical contexts, and
further refining the methods of EIM data acquisition and analysis
|
PROGETTAZIONE E VALIDAZIONE DI PROTOCOLLI
BASATO ESERCIZI A PEDANA VIBRANTE SU SOGGETTI CON PATOLOGIA DI
PARKINSON E SCLEROSI MULTIPLA |
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
The effects of whole-body-vibration
exercises (mechanical oscillations)in
Parkinson´s disease and multiple sclerosis
 
|
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
is a complex, progressive and disabling neurodegenerative disorder
marked by progressive loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons which
is related to a continuous impairment of motor functions.
As pharmacological
treatments (L-Dopa, Dopamin Agonists) are lowly effective with
respect to postural disturbance, and furthermore they lose effectiveness
with disease progression potent nonpharmacologic therapies, are of
crucial importance for the management of impairments.
Approximately 400,000
people in the EU suffer from multiple sclerosis, a disease of the spinal
cord, brain and nervous system that affects motor control, vision,
cognitive function and emotions.
There is no cure for
multiple sclerosis, though various drug and physical therapies may help
to decrease symptoms.
Besides traditional types of exercise, like strength or endurance
training, passive exercise, whole body vibration was found having
positive influence on PD and MS motor symptoms.
As the use of
the oscillating platforms is very inexpensive and positive clinical
findings have been noticed with the use of whole body vibration in
patients with PD, and MS it is suggested to implement the studies
involving the application of the exercises with whole body vibration in
oscillating platforms to manage the patients with PD.
|
STUDIO DEGLI EFFETTI DELLA TOSSINA BOTULINICA
IN DISORDINI MOTORI, DISTONIA,SPASTICITA' |
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
Study of the selectivity
of botulinum toxins (BoNT-A and BoNT-C) for muscle fiber type units and
their kinetics diffusion by exo-endocytosis: electro and impedence
myography evaluation, biochemical pathway analysis and possible clinical
implication in Spasticity, Dystonia, and Related Motor
Disorders
|
Design implementation
and clinical validation of 2D high-density electrode arrays (2DHDEMGs),with
a bi-dimensional grid of 128 electrodes (8x16 with 10 mm interelectrode
distance) positioned on the muscle suitable for recording EMGsurface
signals (array processing) from different types of muscles and analysis
of innervation zone (IZ).
The knowledge of
innervation zone position (IZ) of muscles is crucial to injection the
product (BoNTs) in specific sites of muscle to have more efficacy and
less side effects .
Analyze the effect of blockade of nerve activity, induced by Botulinum
Neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A), that promotes the expression of the slow
isoform of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) in contrast with other
neuromuscular inactivity models; and correlate the MyHC isoform switch
with the muscle fiber denervation by BoNTs to better understand this
phenomenon and to investigate if botulinum neurotoxins block
preferentially some motor units rather than others.
Study of diffusion of different Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT-A and BoNT-C)
formulations injected in the mouse model using an highly sensitive test
based on Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (N-CAM) expression in muscle.
|
STUDIO DEGLI EFFETTI DI ESERCIZIO RIABILITATIVO
ASSISTITO AD ALTA INTENSITA' IN PAZIENTI PARKINSON
|
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
Study of different
types of exercises (randomized controlled trials) of FORCED
EXERCISE (mechanically assisted) in order to minimize the negative
effects of the PD on motor and functional performance

|
Forced Exercise (FE), is a relatively
new approach to exercise in human patients with PD. FE, is defined
operationally as a mode of aerobic exercise in which exercise rate is
augmented mechanically to assist the participant in achieving and
maintaining an exercise rate that is greater than their preferred
voluntary rate of exercise. It is important to note that during FE, the
participant is contributing actively to the exercise; they are not being
moved through the motion passively.
The effects of FE on motor and behavioral function using the 6-OHDA or
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) rodent model of PD
has been studied extensively. [Fisher BE, Petzinger GM, Nixon K, et al.
Exercise-induced behavioral recovery and neuroplasticity in the
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned mouse basal
ganglia. J.
Neurosci. Res. 2004;
77(3):378–90,; Zigmond MJ. Triggering endogenous neuroprotective
mechanisms in Parkinson's disease: studies with a cellular model. J.
Neural Transm. Suppl. 2006; (70):439–42;Zigmond MJ, Cameron JL, Leak RK,
et al. Triggering endogenous neuroprotective processes through exercise
in models of dopamine deficiency. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009;
15(Suppl 3):S42–5.] A typical FE paradigm is motorized treadmill running
that requires the animal to maintain a running velocity that is greater
than its preferred running velocity.
|
STUDIO DEGLI EFFETTI DI UNA SUPPLEMENTAZIONE DI
AMINOACIDI ARRICCHITI CON LEUCINA IN PAZIENTI CON SCLEROSI LATERALE
AMIOTROFICA
|
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
Effect of branched-chain amino acid
(BCAA) supplementation enriched of leucine (LEU)in amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis patients
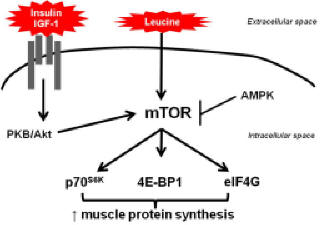
|
A prospective
randomized double-blind study was performed with 12 male PALS,
( ranging between 44 and 63 y.o.) divided into two groups: the treatment
group (T) received BCAA supplementation (80 mg/kg bodyweight/day with
ratio leucine/isoleucine/valine of 6/1/1), whereas the control group (C)
received placebo (similar enriched flavours) .
ALS patients meeting
El Escorial criteria for defined disease, either with bulbar or
appendicular onset, regularly assisted in the Clinic, were included in
the study. Patients with nasogastric tube or gastrostomy, on assisted
mechanical ventilation and without intervening neurological illnesses.
Body weight (kg) and height (m) were assessed ,Body mass index (BMI -
kg/m2) and midarm circumference (MAC - cm), were determined;
The tricipital (TSF),
skinfolds were measured using the scientific Lange branded
(0.1mm-accuracy adipometer) midarm muscle circumference (MAMC), arm
muscle area (AMA) and arm fat area (AFA) were obtained from MAC and TSF
according to Heymsfield et al. The percentage of weight loss (%WL) was
determined based upon the usual and the actually measured weight of the
patient. BIA was performed by measuring the bioimpedances at 50 kHz and
FFM was calculated by using TSF and Desport equation.
We determined the
serum levels of albumin, pre-albumin, creatine-kinase (CK), creatine,
urea, glucose, aspartate transferase (AST), alanine transferase (ALT),
total lymphocyte count, platelets, sodium and potassium for each patient.
All measurements were taken before (baseline), every 4 months (mid-points)
and at the end of the trial (end – point) .
|
STUDIO DELLA ANALISI BIOIMPEDENZIOMETRICA
SEGMENTALE E CORRELAZIONE CON SPESA ENERGETICA A RIPOSO IN PAZIENTI CON
SCLEROSI LATERALE AMIOTROFICA
|
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
Correlation among Forced Vital
Capacity (FVC), Resting Energy Expenditure (REE) and segmental trunk
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (stBIA) in ALS patients for predicting
clinical disease progression: a preliminary study
 |
In als patients
(mean age ± SD: 52.1 ± 11.5 yrs; 7 M; 5 F) with definite ALS, neurologic
deficit was quantified by manual muscular testing of all extremities and
the neck as defined by the Medical Research Council.
All patients were
stable in pharmacological medication (50 mg riluzole twice a day); no
patient received any steroid drug treatment. FVC was measured with a
pneumotachograph system (Medical Graphics, St Paul): findings were
expressed in relation to a theoretical calculated index value.
Indirect calorimetry
was performed with a VO2000 (Medical Graphics, St Paul) that was
calibrated each morning before the measurements were made. Measurements
were accepted if the results were at a stable plateau for ≥ 20 min.
The measured REE (mREE)
was compared with REE obtained from a control population volunteers and
with REE calculated (cREE) by using the Harris-Benedict equations. In
stBIA, (50 kHz) the 4 source electrodes and the combination of 8
detecting electrodes used in this study allowed to separate the trunk
into 5 parts and determine the Z of each part. All PALS were tested each
6 months: in such a preliminary work a 24-month period was analyzed.
|
UTILIZZO DELLA MIOGRAFIA ULTRASONOGRAFICA NELLA
SCLEROSI LATERALE AMIOTROFICA
|
SCOPO DEL PROGETTO
|
|
QUANTITATIVE MUSCLE ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL
SCLEROSIS
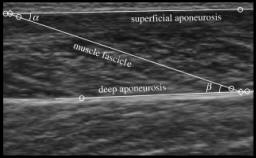
|
In this study, we
examined whether quantitative muscle ultrasonography can detect
structural muscle changes in early-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(ALS).
Bilateral transverse
scans were made of five muscles or muscle groups (sternocleidomastoid,
biceps brachii/brachialis, forearm flexor group, quadriceps femoris and
anterior tibialis muscles) in patients with ALS.
Quantitative
analysis revealed a significant increase in echo intensity in all muscles
and a decrease in muscle thickness of the biceps brachii, forearm flexors
and quadriceps femoris on both sides.
Fasciculations were
easy to detect in multiple muscles of all screened patients except one.
Quantification of
muscle thickness and echo intensity provides a sensitive and specific
objective method to discriminate between neuromuscular and
non-neuromuscular disease.
We conclude that
quantitative ultrasonography can be used to detect muscle changes caused
by ALS in an early phase of the disease |
|